HMI Full Form & What HMI Software: The Complete Guide
Updated on : 16 May, 2025

Image Source: google.com
Table Of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. HMI Full Form: What Does HMI Stand For?
- 3. What is HMI Software?
- 4. How HMI Software Works
- 5. Key Features of HMI Software
- 6. Architecture and Communication
- 7. Benefits of Using HMI Software
- 8. Common Use Cases and Industries
- 9. HMI vs. SCADA vs. PLC
- 10. What are the benefits of custom HMI software development?
- 11. Trends and Future of HMI
- 12. Best Practices for HMI Implementation
- 13. How HMI software enables smart manufacturing
- 14. FAQs
- 15. Conclusion
Table Of Contents
Introduction
HMI is the digital dashboard that allows a human operator to monitor, control, and communicate with machines. This interface can take many forms—such as touchscreens, computer displays, tablets, or mobile devices—and displays real-time data like temperatures, pressures, motor speeds, or machine status. It also allows operators to send commands such as starting or stopping a machine, adjusting settings, or resetting alarms.

Image Source: google.com
Connect Today with Hexadecimal Software for Human Machine Interface(HMI) Services
From touch to tech, Hexadecimal Software redefines HMI. Experience the power of innovation at your fingertips!
HMI Full Form: What Does HMI Stand For?
HMI stands for Human-Machine Interface — a vital component that bridges the gap between people and machines.
Whether it's a factory floor, automated assembly line, or even a power plant, HMIs provide a digital interface that allows human operators to monitor, control, and optimize machine performance through interactive displays.
| Type of HMI | Description | Docs |
|---|---|---|
| Touchscreen Panels | Interactive panels used to control machinery and display live system data. | Rockwell PanelView |
| Computer Dashboards | Software-based dashboards with real-time controls, graphs, and alerts. | Ignition Docs |
| Mobile Devices | Tablets or smartphones with HMI apps for remote monitoring and control. | Siemens Mobile HMI |
| Wearable Devices | Smart glasses or AR headsets for hands-free machine supervision. | RealWear |
| Button Replacers | HMIs that eliminate the need for physical buttons and switches. | Pro-face HMIs |
What is HMI Software?

Ready to elevate reality with next-gen AR/VR solutions?
HMI software is the technology that powers the interface between operators and machines. It provides a graphical user interface (GUI) that allows users to visualize data, send commands, and monitor processes in real time. HMI software is essential for executing commands, controlling machinery, and managing manufacturing or production processes.
What It Does:
-
Shows real-time data from machines (e.g., speed, temperature, status)
-
Lets the operator start, stop, or adjust machine operations
-
Sends alerts or warnings if something goes wrong
-
Helps with remote control and automated processes
Real-Life Example: Car Dashboard = HMI
Imagine you’re sitting in your modern car. The dashboard in front of you is a perfect example of HMI in action!
| Car Feature | HMI Role | Docs |
|---|---|---|
| Touchscreen display | Shows music, maps, temperature – lets you control features with your finger | Bosch Infotainment |
| Speedometer, fuel gauge, engine lights | Displays real-time data from the car’s sensors | Nippon Seiki Displays |
| Buttons for lights, AC, and wipers | Let you operate the car using simple inputs | Continental HMI |
| Voice assistant or steering controls | Offers smart control for safety and convenience | Nuance Automotive Voice |
How HMI Software Works
HMI (Human-Machine Interface) software works by bridging the communication gap between industrial machinery and human operators, usually through integration with a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC).
Here's how it works in practice:
-
Industrial machines are controlled by PLCs, which automate tasks like movement, speed, temperature control, etc.
-
The HMI software connects to these PLCs so that when an operator interacts with the HMI dashboard (e.g., adjusts a setting), the PLC executes the command in real time.
-
For example, in a conveyor belt system, an operator can use the HMI to change the belt’s speed or direction. The PLC interprets this input and controls the belt accordingly.
-
Many systems also include sensors, cameras, and feedback mechanisms. These gather data and send it to the HMI interface, giving operators real-time insights for decision-making.
-
Modern HMI systems are often cloud-connected and use wireless communication, allowing remote monitoring and control via touchscreen panels, PCs, or mobile devices.
Types of HMI Systems

Image Source: google.com
| Type | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Data Handler | Collects, displays, and manages data with logging, alarms, charts, and trends. | Real-time monitoring and reporting |
| Pushbutton Replacer | Replaces physical buttons and switches with a digital interface. | Basic machine control (e.g., start/stop) |
| Overseer | Visual, software-rich interface integrated with SCADA, Windows, or mobile apps. | Large-scale supervision and MES systems |
Explore Cloud Computing Service
You Might Also Like
Key Features of HMI Software
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Customizable Screens | Design dashboards tailored to specific tasks or users |
| Real-Time Visualization | Display live process data, trends, and KPIs |
| Input/Output Control | Trigger machine actions or adjust parameters |
| Alarm & Event Handling | Monitor for issues and send notifications |
| Data Collection & Logging | Store historical data for analysis |
| Remote Access | Monitor and control systems from anywhere |
| Security | Role-based access, encryption, and activity logs |
| Integration | Connect with PLCs, SCADA, MES, and IIoT protocols |
Architecture and Communication
HMI software architecture is designed to enable seamless interaction between human operators and industrial machines through multiple layers of hardware and software components. It ensures reliable data flow, real-time control, and monitoring across complex industrial environments.
Key Components of HMI Architecture:
User Interface Layer
- This is the front end visible to the operator.
- It typically includes dashboards, graphical displays, control panels, and input devices like touchscreens, keyboards, or buttons.
- It presents data visually and allows operators to send commands to machines.
Application Layer
-
The core HMI software resides here, managing the visualization, logic, and processing of inputs and outputs.
-
This layer interprets operator commands and communicates them to the control system, while also receiving and processing real-time data from the machines.
Control Layer (PLC/Controller)
-
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) or other controllers execute commands from the HMI software and operate machinery accordingly.
-
They gather data from sensors and machines and send feedback to the HMI for monitoring.
Communication Layer
-
Facilitates data exchange between the HMI software, PLCs, sensors, and other devices.
-
Can use wired protocols (Ethernet, RS-232/485, Modbus) or wireless connections (Wi-Fi, cellular, Bluetooth).
-
Often involves cloud servers for remote access, data analytics, and integration with IoT platforms.
Explore IoT Development Services with Hexadecimal Software
Benefits of Using HMI Software
| Benefit | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Improved Efficiency | Operators spot problems quickly and optimize processes |
| Reduced Downtime | Real-time monitoring and alarms speed up response |
| Enhanced Data Visibility | Visual dashboards make complex data easy to understand |
| Remote Management | Control and monitor systems from anywhere |
| Better Decision-Making | Access to historical and real-time data aids analysis |
| Scalability | Future-proof solutions grow with your business |
Common Use Cases and Industries
| Use Case | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| CNC Lathes | Control and monitor cutting machines | Fewer errors, higher output |
| Plastic Molding | Manage heat and motion in molding | Safer, precise control |
| Robotic Arm Control | Remote control and supervision | Enhanced safety, remote ops |
CNC Lathes
- CNC (Computer Numerical Control) lathes are machines that precisely shape materials like metal or wood by rotating the workpiece and applying cutting tools.
- Traditionally, these machines are controlled using physical buttons, LEDs, and fixed monitors, which can be complex and prone to human error.
- With HMI software, operators can control and monitor these machines more easily through an intuitive touchscreen interface.
- This reduces mistakes, improves precision, and increases overall productivity by allowing faster adjustments and real-time feedback on machine status.
Plastic Molding
- Plastic molding processes, such as injection molding, extrusion, and thermoforming, involve handling high temperatures and potentially toxic chemicals.
- These conditions can be hazardous for operators.
- HMI software integrates with the machine��’s control systems (like PLCs) to precisely regulate temperature, pressure, and motion remotely.
- This ensures safer working conditions, better quality control, and reduces risks associated with manual operation of dangerous machinery.
Robotic Arm Control
- In many manufacturing assembly lines, robotic arms perform repetitive or dangerous tasks.
- While many operations are automated, some require human supervision or manual control for safety or precision.
- HMI software combined with Augmented Reality (AR) enables operators to control or oversee robotic arms remotely, from a safe distance.
- This technology enhances safety by minimizing operator exposure to hazardous environments, while also allowing precise and efficient handling of complex assembly tasks.
HMI vs. SCADA vs. PLC
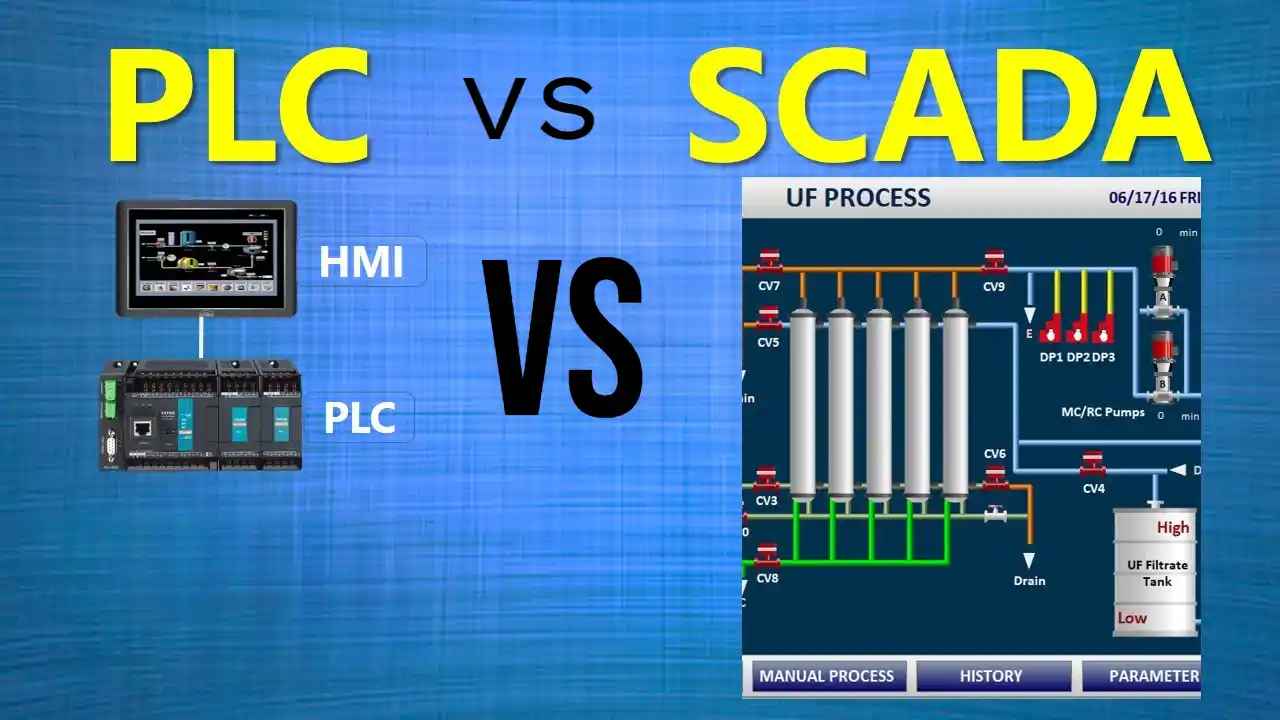
Image Source: google.com
| System | Role | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| HMI | User interface for machine control and monitoring | Single machine or process |
| SCADA | Supervisory control and data acquisition | Multiple sites, enterprise-wide |
| PLC | Programmable logic controller for automation | Equipment-level control |
HMI (Human-Machine Interface):
-
Provides an intuitive visual dashboard for operators.
-
Controls and monitors a single machine or process.
-
Displays real-time data and allows manual inputs.
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition):
-
Manages and supervises multiple machines or entire plants.
-
Collects and analyzes data across various locations.
-
Enables remote monitoring and control for enterprise-wide systems.
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller):
-
Executes automation tasks by controlling machine functions.
-
Processes input from sensors and sends commands to actuators.
-
Works at the equipment level for precise and reliable control.

Need expert guidance in building intuitive HMI solutions for your systems?
What are the benefits of custom HMI software development?
Benefits of Custom HMI Software Development
Ease of Use:
-
Uses intuitive touchscreen interfaces instead of complex buttons and switches.
-
Simplifies machine operation for both new and experienced users.
-
Reduces the learning curve for operators, speeding up training.
Increased Productivity and Efficiency:
-
Centralizes control of machines on one dashboard.
-
Eliminates the need for operators to move between different control panels.
-
Enables quicker decision-making with real-time data visualization.
Improved Employee Safety:
-
Allows remote control, keeping operators away from hazardous machinery.
-
Uses cameras and sensors for visual inspections without physical proximity.
-
Minimizes direct contact with toxic or dangerous materials.
Increased Reliability:
-
Provides real-time monitoring through connected sensors and cameras.
-
Supports predictive maintenance to prevent unexpected machine failures.
-
Helps managers make informed decisions to improve uptime.
Fewer Human Errors:
-
Automates routine controls to reduce manual mistakes.
-
Sends alerts to prevent operators from missing critical warnings.
-
Offers a clear, user-friendly interface to avoid confusion.
Reduced Costs:
-
Cuts down maintenance expenses by detecting problems early.
-
Saves money on staff training due to easy-to-learn software.
-
Minimizes costly machine downtime through better reliability.
High Return on Investment (ROI):
-
Low initial setup cost compared to long-term savings.
-
Improves overall productivity, leading to higher profits.
-
Reduces operational costs, quickly offsetting the investment.
Trends and Future of HMI
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Touchscreen and Gesture Control | Moving from physical buttons to intuitive touch and gesture-based controls for easier use. |
| Voice Recognition and AI Integration | Using voice commands and AI to enable hands-free operation and smarter decision-making. |
| Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) | Immersive 3D visuals for machine control, maintenance, and operator training. |
| Edge Computing and IoT Connectivity | Processing data locally on edge devices for faster, real-time industrial control. |
| Cloud Integration and Remote Access | Centralized data and remote machine monitoring through cloud platforms. |
| Enhanced Security Features | Strong cybersecurity measures to protect industrial systems as connectivity increases. |
| Customization and Scalability | Flexible, customizable interfaces that scale for different industries and complex setups. |
Explore AR/VR Services with Hexadecimal Software
Best Practices for HMI Implementation
Design intuitive, uncluttered dashboards
- Create user interfaces that are simple and easy to navigate.
- Avoid overcrowding the screen with too much information so operators can quickly find and understand what they need.
- A clean design helps reduce confusion and speeds up decision-making.
Use clear visualizations and color codes for alarms
- Represent data using graphs, charts, and symbols that are easy to interpret at a glance.
- Use standardized colors—like red for critical alarms and yellow for warnings—to help operators immediately recognize issues and prioritize responses.
Implement robust security and access controls
- Protect the HMI system from unauthorized access by setting up strong passwords, user roles, and permissions.
- Secure communication channels and regularly monitor for vulnerabilities to prevent cyber-attacks that could disrupt operations or cause safety risks.
Regularly update software for new features and security patches
- Keep the HMI software up to date to benefit from improved functionality, bug fixes, and the latest security protections.
- Timely updates ensure your system stays reliable, efficient, and resistant to emerging threats.
Train operators for maximum efficiency
- Provide thorough training to users so they understand how to operate the HMI software effectively.
- Well-trained operators can respond faster, avoid errors, and make the most of the system’s capabilities, boosting overall productivity and safety.
How HMI software enables smart manufacturing
HMI (Human-Machine Interface) software is a key driver in the shift toward Industry 4.0 and beyond, playing a central role in modernizing manufacturing systems. Here’s how it contributes to smart manufacturing:
| Feature | How It Enables Smart Manufacturing |
|---|---|
| Digital Control & Automation | Replaces manual controls with touchscreen dashboards for real-time machine monitoring and control. |
| AI & ML Integration | Supports intelligent automation, predictive maintenance, and smart decision-making using AI/ML models. |
| Cloud-Based Access | Operators can access and control machinery remotely, reducing downtime and increasing flexibility. |
| Real-Time Data Visualization | Live graphs and alerts help operators quickly react to issues and optimize processes. |
| Seamless PLC Integration | Communicates with controllers to execute commands and collect sensor data efficiently. |
| Enhanced Safety & Reliability | Remote monitoring reduces physical contact with hazardous machinery, increasing safety. |
| Custom Dashboards | Tailored UIs allow for operator-specific views and process customization. |
| Improved Efficiency & Productivity | Faster responses, fewer errors, and automated workflows result in better overall output. |
| Cost Reduction | Less downtime, predictive maintenance, and reduced errors lead to lower operational costs. |
| Scalability for Future Tech | Easily integrates with robotics, AR, digital twins, and IoT for factory evolution. |
Explore AI/ML Services with Hexadecimal Software
FAQs
Q.1. What is HMI software?
A: It’s a digital tool that lets humans control and monitor machines through screens and dashboards.
Q.2. How does HMI help in manufacturing?
A: It improves efficiency, reduces errors, and makes machine control easier and safer.
Q.3. Can HMI work with old machines?
A: Yes, it connects with PLC systems that control older machines.
Q.4. Is HMI safe to use?
A: Modern HMI systems have strong security features like passwords and updates.
Q.5. What are the main benefits of HMI?
A: Better productivity, less downtime, and safer working conditions.
Q.6. Can HMI be used remotely?
A: Yes, cloud-based HMI allows monitoring and control from phones or computers.
Conclusion
Human-Machine Interface (HMI) Software plays a critical role in modern industrial automation. It bridges the gap between humans and machines, making operations more efficient, safe, and intuitive. With the integration of technologies like cloud computing, AI, and PLCs, HMI solutions are shaping the future of smart manufacturing. From controlling robotic arms to optimizing CNC machines, HMI software improves productivity, reduces errors, and cuts operational costs. As industries move toward Industry 5.0, investing in smart, custom HMI systems is not just beneficial—it’s essential.







