Top Web App Databases 2025: Best SQL & NoSQL Options
Updated on : 17 March 2025

Image Source: google.com
Table Of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. What Is a Web Application Database?
- 3. Best Databases for Web Applications in 2025
- 4. Benefits of Gamified Fitness Experiences
- 5. SQL vs. NoSQL: Which One to Choose?
- 6. Key Considerations When Selecting a Database
- 7. Security Features of Different Databases
- 8. Cloud-Based vs. On-Premises Databases
- 9. What Is the Easiest Database to Use?
- 10. Which Database Is Best for Python?
- 11. Trends in Web App Databases for 2025
- 12. Future of Databases and Emerging Technologies
- 13. Concluding Thoughts
- 14. FAQs
Table Of Contents
Introduction
When developing a web application, selecting the right database is crucial for performance, scalability, and ease of use. With numerous options available, it’s essential to understand the best database solutions suited for web applications in 2025 and beyond.
What Is a Web Application Database?
A web application database is a structured collection of data that enables applications to store, retrieve, and manage information efficiently. Depending on the needs of the application, databases can be relational (SQL) or non-relational (NoSQL). Web databases serve various functions, including user authentication, content management, transaction handling, and analytics.
Web app development creates interactive, browser-based applications for seamless user experiences.
Best Databases for Web Applications in 2025
Here’s a list of the top databases for web applications, along with their use cases, advantages, and drawbacks.

Image Source: google.com
Choosing the Right Database for Your Web Application
🔹 For High Scalability & NoSQL Flexibility → MongoDB, DynamoDB, Firebase
🔹 For Data Integrity & Complex Queries → PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB
🔹 For Real-Time Performance & Caching → Redis, Firebase, Cassandra
🔹 For Graph & Relationship-Based Applications → Neo4j

Looking to enhance your business with professional website design and development?
SQL vs. NoSQL: Which One to Choose?
Relational Databases (SQL) Overview
SQL databases store data in structured tables, ensuring consistency and integrity through ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) compliance. They are best suited for applications requiring structured queries, such as eCommerce and banking.
| Database | Type | Best For | Pros | Cons | Official Documentation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oracle | Relational | Large enterprises, banking, financial systems | Advanced security, excellent performance | Expensive licensing, complex setup | Oracle Docs |
| MySQL | Relational | Small to medium-sized applications, CMS | Free, open-source, strong community support | Limited scalability for very large apps | MySQL Docs |
| MS SQL Server | Relational | Enterprise, Windows-based apps | High availability, excellent security | Costly licensing, Windows dependency | MS SQL Docs |
| PostgreSQL | Relational | Data-intensive applications, analytics | ACID compliance, JSON support, high performance | Complex configuration | PostgreSQL Docs |
| IBM DB2 | Relational | Enterprises, data warehousing | AI integration, reliability | High costs, complex learning curve | IBM DB2 Docs |
| MariaDB | Relational | Web applications needing MySQL alternatives | Better performance than MySQL, open-source | Some compatibility issues with MySQL features | MariaDB Docs |
| SQLite | Relational | Mobile apps, embedded systems | Self-contained, serverless, easy setup | Not scalable for large applications | SQLite Docs |
| FirebirdSQL | Relational | Small applications, embedded systems | Lightweight, cross-platform support | Limited scalability | Firebird Docs |
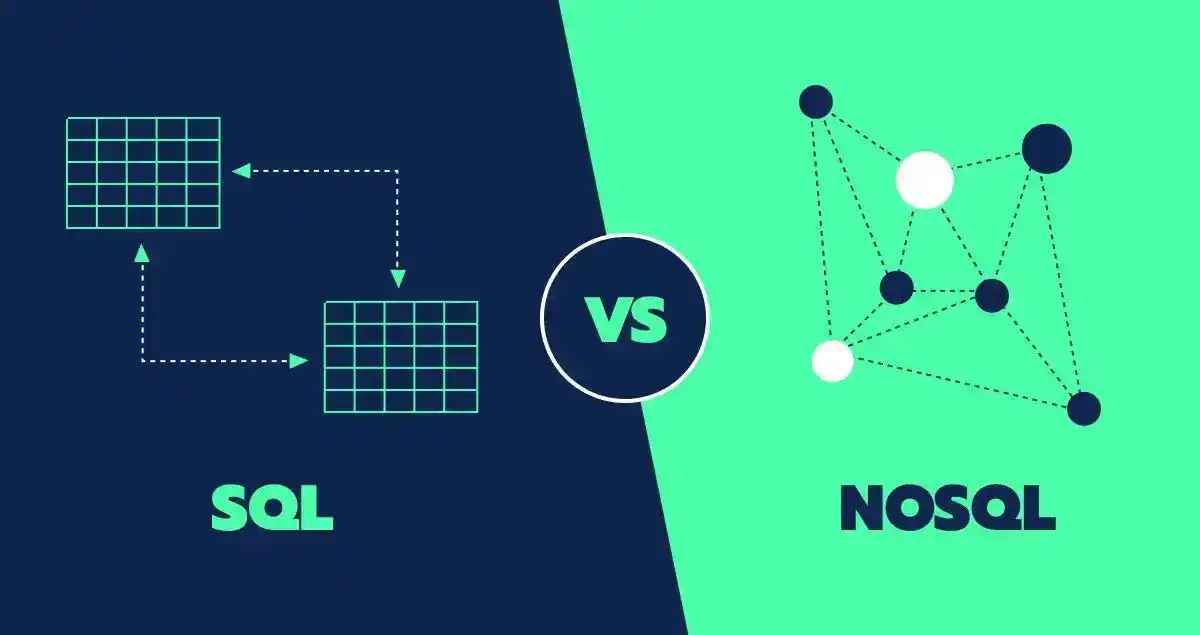
Image Source: google.com
Non-Relational Databases (NoSQL) Overview
NoSQL databases store data in flexible formats like key-value, document, column-family, or graph structures. They are ideal for handling unstructured or semi-structured data and are widely used in real-time analytics, social networks, and IoT applications.
| Database | Type | Best For | Pros | Cons | Official Documentation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MongoDB | NoSQL (Document) | Real-time apps, IoT, CMS | Flexible schema, scalable, high availability | High memory usage, lacks ACID compliance | MongoDB Docs |
| Redis | Key-Value Store | Caching, session management, real-time apps | Super-fast performance, supports various data structures | Not suitable for transactional applications | Redis Docs |
| Elasticsearch | Search Engine | Search-driven applications, log analysis | High-speed searching, scalability | Requires additional databases for storage | Elasticsearch Docs |
| Cassandra | NoSQL (Column) | Big data, real-time analytics | High availability, excellent write performance | Complex management, no ACID compliance | Cassandra Docs |
| OrientDB | Multi-Model (Graph, Document) | Social networks, recommendation systems | Hybrid approach, fast graph queries | Complex setup and maintenance | OrientDB Docs |
| DynamoDB | NoSQL (Key-Value) | Serverless apps, real-time data processing | Fully managed, high scalability | High costs for heavy usage | DynamoDB Docs |
| Neo4j | Graph | Fraud detection, recommendation engines | Optimized for connected data, efficient queries | Not ideal for traditional relational data | Neo4j Docs |
Key Considerations When Selecting a Database

Enhance your business with scalable and high-performance database solutions!
| Factor | SQL Databases | NoSQL Databases |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Vertical Scaling | Horizontal Scaling |
| Data Structure | Structured | Flexible |
| Performance | Consistent read performance | Fast write operations |
| Use Cases | Banking, enterprise apps | Big data, real-time apps |
Security Features of Different Databases
Security is a major factor when choosing a database. Enterprise databases like Oracle and MS SQL Server offer built-in encryption, authentication mechanisms, and compliance with data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). Open-source databases like MongoDB and Elasticsearch require additional configurations to secure data properly, such as enabling TLS encryption and setting up authentication controls.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premises Databases
- Cloud-Based Databases (e.g., DynamoDB, Firebase) offer automatic scalability, low maintenance, and built-in security features.
- On-Premises Databases (e.g., Oracle, MS SQL Server) provide more control over security, compliance, and performance but require more management.
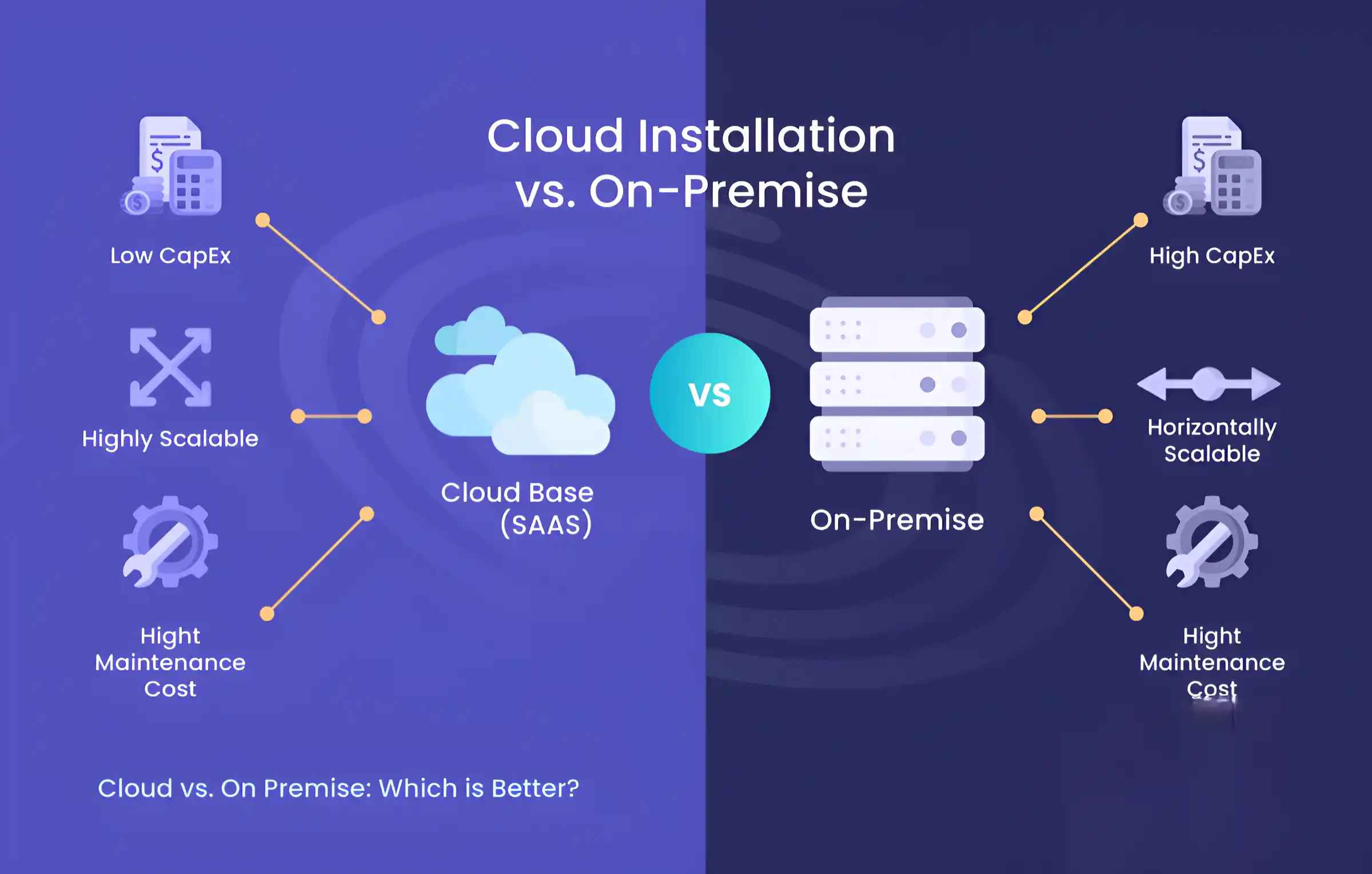
Image Source: google.com
Cloud services provide scalable, on-demand computing resources for storage, processing, and application hosting.
What Is the Easiest Database to Use?
SQLite is the simplest to set up, as it is serverless and requires no configuration. It is ideal for small projects, prototypes, and local storage in mobile and desktop applications.
Which Database Is Best for Python?
Python developers frequently use:
- SQLite – Lightweight, easy to use for small projects.
- PostgreSQL – Powerful and feature-rich for large applications.
- MongoDB – NoSQL flexibility for handling unstructured data.
Trends in Web App Databases for 2025
- AI-Driven Databases – Automated query optimization with AI (e.g., IBM DB2, Oracle).
- Serverless Databases – Fully managed services like DynamoDB and Firebase.
- Graph Databases Growth – Neo4j gaining traction for social networks and fraud detection.
- Multi-Model Databases – Combining relational, document, and graph data models.
- Edge Computing Databases – Lightweight databases like SQLite and Firebase optimizing for edge devices.
Future of Databases and Emerging Technologies
As technology evolves, databases will integrate AI-driven query optimization, blockchain-based data integrity, and support for real-time analytics at scale. The demand for highly available, globally distributed databases will continue to rise.
Concluding Thoughts
Choosing the best database for your web application depends on your project’s needs:
- Relational databases: PostgreSQL and MySQL for structured data.
- NoSQL databases: MongoDB and DynamoDB for flexibility.
- In-memory databases: Redis for speed.
- Big data solutions: Cassandra and Elasticsearch.
Carefully evaluate scalability, security, and cost before selecting a database. With the right choice, you can ensure optimal performance and long-term success for your web application.
FAQs
Q.1. What is a web application database?
A: A database that stores and manages data for web applications, enabling dynamic content and user interactions.
Q.2. Which database is best for web applications in 2025?
A: It depends on the use case, but PostgreSQL, MySQL, and MongoDB are top choices.
Q.3. What are the key benefits of gamified fitness experiences?
A: Increased user engagement, motivation, and personalized workout tracking.
Q.4. How do SQL and NoSQL databases differ?
A: SQL is structured and relational, while NoSQL is flexible and suited for unstructured data.
Q.5.What are the security features of different databases?
A: Encryption, access control, authentication, and automated backups enhance security.
Q.6. Which database is easiest to use for beginners?
A: SQLite is one of the simplest databases, requiring minimal setup and administration.


