Software Bug Life Cycle Complete Beginners Guide
Updated on : 21 AUGUST 2025
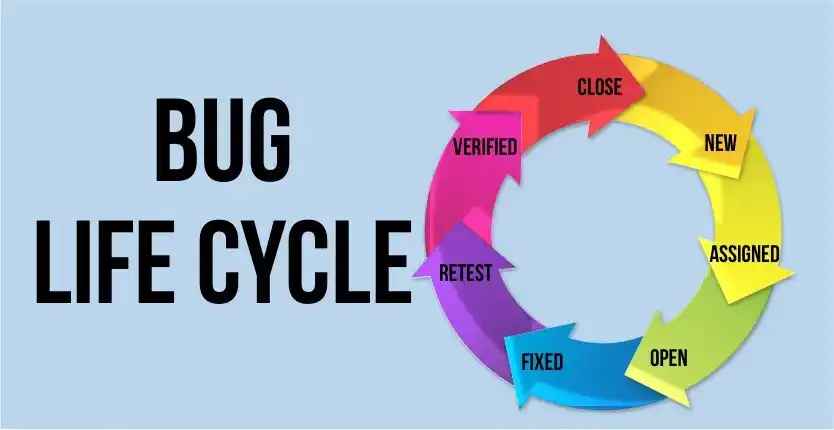
Image Source: google.com
Table Of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. What is a Bug Life Cycle?
- 3. Bug Life Cycle Stages
- 4. New State (Bug Reported)
- 5. Assigned State (Developer Ownership)
- 6. Open State (Under Fixing)
- 7. Fixed State (Developer Fix)
- 8. Retest State (Tester Verification)
- 9. Verified State (Confirmed Fixed)
- 10. Closed State (Final Closure)
- 11. Reopened State (If Issue Persists)
- 12. Bug Status Transition Table
- 13. Best Practices in Bug Tracking
- 14. FAQs
Table Of Contents
Introduction
In software testing, a bug lives a journey of its own! 🐞 From being reported New , assigned to a developer Assigned , worked on Open , fixed , retested , Verified , and finally Closed — each stage ensures better quality software delivery. Sometimes, the bug comes back Reopened if not fixed properly.
What is a Bug Life Cycle?
The bug life cycle (or defect life cycle) is the process of tracking the status of a bug from discovery to closure.
It ensures:
- Proper communication between testers and developers
- Transparency in defect handling
- Faster resolution of issues
Bug Life Cycle Stages
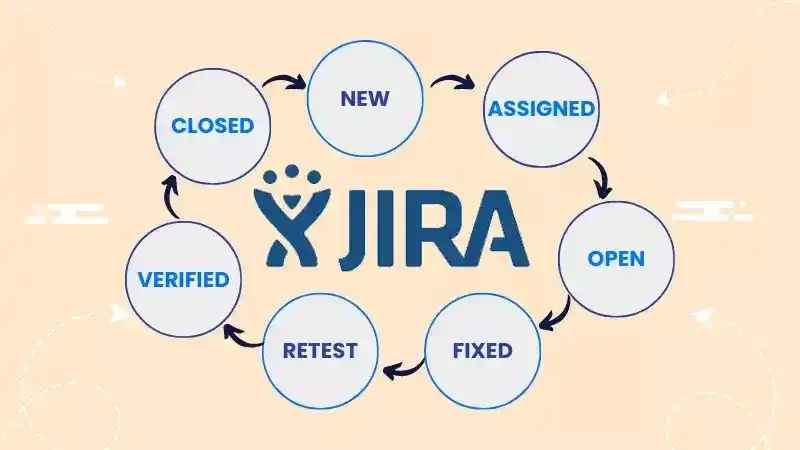
Image Source: google
| State | Description |
|---|---|
| New | Bug is identified and reported by tester |
| Assigned | Bug is assigned to a developer for fixing |
| Open | Developer starts working on the bug |
| Fixed | Developer resolves the bug |
| Retest | Tester verifies if fix works |
| Verified | Tester confirms the bug is resolved |
| Closed | Bug is officially marked as resolved |
| Reopened | Bug resurfaces after being marked closed |
For Quality Assurance Testing Services with Hexadecimal Software
New State (Bug Reported)
| New State |
|---|
| A tester finds a defect and logs it in a bug tracking tool (like Jira, Bugzilla, or Redmine) |
| Bug contains: Steps to reproduce, Severity, Priority, Screenshots, Environment details |
| Status: New |
Example: "Login button does not redirect to dashboard page."
Assigned State (Developer Ownership)
| Assigned State |
|---|
| Once reviewed by the QA lead or project manager, the bug is assigned to a developer |
| Status: Assigned |

Need help managing QA and Bug Tracking?
Open State (Under Fixing)
| Open State |
|---|
| The developer starts analyzing and working on the bug |
| The bug status is changed to Open |
| Developer investigates root cause and applies code changes |
Fixed State (Developer Fix)
| Fixed State |
|---|
| After resolving the defect, the developer marks the bug as Fixed |
| The code is then moved to QA for retesting |
You Might Also Like
Retest State (Tester Verification)
| Retest State |
|---|
| QA team retests the functionality to confirm the bug is resolved |
| If the fix is successful → Bug moves to Verified |
| If not → Bug moves to Reopened |
Verified State (Confirmed Fixed)
| Verified State |
|---|
| If the fix works as expected and no issues remain, the tester updates bug status to Verified |
Closed State (Final Closure)
| Closed State |
|---|
| After successful verification, the bug is marked as Closed. |
| No further action is needed unless issue reappears. |
Reopened State (If Issue Persists)
| Reopened State |
|---|
| If the bug still exists after being marked Closed, it is Reopened. |
| Developer re-checks and fixes it again. |
Bug Status Transition Table
| From State | To State | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| New | Assigned | Bug assigned to developer |
| Assigned | Open | Developer starts working |
| Open | Fixed | Bug resolved by developer |
| Fixed | Retest | QA retests the bug |
| Retest | Verified | Fix works correctly |
| Retest | Reopened | Bug still exists |
| Verified | Closed | Bug is confirmed and closed |
| Closed | Reopened | Bug reappears during later testing |

Looking for Expert QA and Testing Services?
Best Practices in Bug Tracking
| ✅ Best Practice | 💡 Benefit |
|---|---|
| Clearly log bug details | Helps developers reproduce issues easily |
| Assign priority and severity | Ensures critical issues are fixed first |
| Keep communication clear | Avoids misunderstanding between QA and Dev |
| Use proper bug tracking tools | Improves visibility and tracking |
| Retest fixes carefully | Ensures bug is really solved |
| Avoid duplicate bugs | Saves time and effort |
| Attach logs/screenshots | Speeds up debugging |
| Close bugs only after verification | Maintains product quality |
FAQs
Q.1. What is a bug life cycle in software testing?
A : It is the process that defines the stages a bug goes through from discovery to closure.
Q.2. What is the first stage of the bug life cycle?
A : The first stage is the New state when the tester reports a bug.
Q.3. Can a closed bug be reopened?
A : Yes, if the issue reappears during retesting or later testing.
Q.4. What is the difference between Verified and Closed states?
A : Verified means the tester has confirmed the fix. Closed means the issue is officially marked resolved.
Q.5. Who assigns a bug to a developer?
A : Usually the QA lead or project manager assigns the bug.
Q.6. What is the Reopened state in a bug life cycle?
A : When a previously fixed bug appears again, it is marked as Reopened.
Q.7. What tools are commonly used for bug tracking?
A : Jira, Bugzilla, Redmine, Mantis, Trello, etc.





