IT Test Cases: Definition, Types, and Best Practices
Updated on : 6 AUGUST 2025

Image Source: google.com
Table Of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. What is a Test Case?
- 3. Purpose of Test Cases in Software Testing
- 4. Key Components of a Test Case
- 5. Types of Test Cases
- 6. Example of a Test Case
- 7. How to Write Effective Test Cases
- 8. Test Case Lifecycle
- 9. Best Practices for Creating Test Cases
- 10. Manual vs Automated Test Cases
- 11. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- 12. Importance of Test Cases in QA
- 13. FAQs
Table Of Contents
Introduction
IT test cases are the backbone of software testing. They define clear steps, expected outcomes, and help testers validate whether software features work as intended. Without test cases, testing would be inconsistent, incomplete, and prone to missing critical bugs.
What is a Test Case?

Image Source: google.com
| What is a Test Case? |
|---|
| Definition : A test case is a documented set of actions, inputs, and expected outcomes designed to verify whether a software application or feature functions correctly. |
| Goal : To ensure that the software meets its requirements and behaves as expected in different scenarios. |
| Usage : Test cases guide testers during manual or automated testing, ensuring consistent results. |
Purpose of Test Cases in Software Testing
| Purpose of Test Cases |
|---|
| 1. Requirement Verification – Confirms that the software meets specified requirements. |
| 2. Bug Detection – Helps identify defects early in the development cycle. |
| 3. Test Coverage – Ensures all features and edge cases are validated. |
| 4. Consistency – Provides structured, repeatable testing steps. |
| 5. Documentation – Serves as a reference for future maintenance and regression testing. |
For Quality Assurance Testing Services with Hexadecimal Software
Key Components of a Test Case
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Test Case ID | Unique identifier for tracking the test case. |
| Title | Short, descriptive name for the test case. |
| Preconditions | Setup or state needed before test execution. |
| Test Steps | Sequential actions to execute during the test. |
| Test Data | Input values used during testing. |
| Expected Result | Outcome expected from the software after steps are executed. |
| Actual Result | Outcome observed after test execution. |
| Status | Pass or Fail based on comparison of results. |

Ensure flawless performance with Hexadecimal’s expert Testing Services.
Types of Test Cases
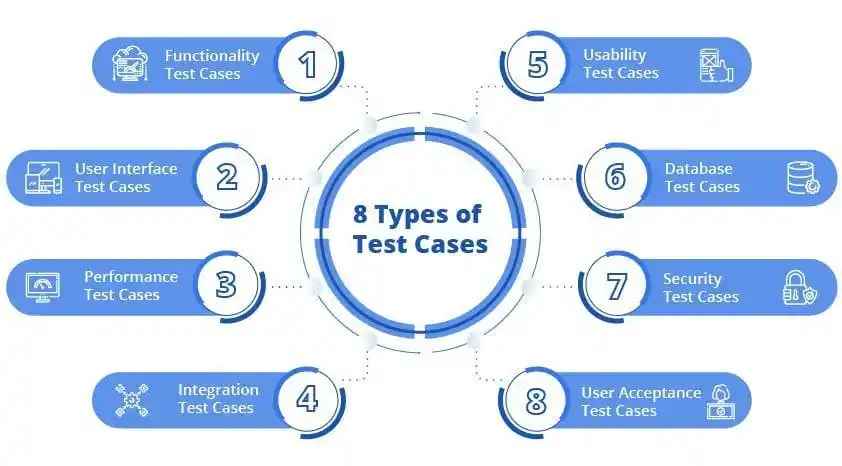
Image Source: google.com
| Test Case Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Functional Test Cases | Validate specific functions of the software. |
| UI Test Cases | Check usability, interface elements, and design. |
| Integration Test Cases | Verify data flow between connected modules. |
| Regression Test Cases | Ensure new changes don’t break existing features. |
| Negative Test Cases | Test the system's behavior with invalid inputs. |
| Performance Test Cases | Measure speed, scalability, and load handling. |
| Security Test Cases | Validate protection against threats and vulnerabilities. |
| User Acceptance Test Cases | Ensure the product meets business needs. |
Example of a Test Case
Title: Verify login functionality with valid credentials.
Test Steps:
- Navigate to the login page.
- Enter a valid username and password.
- Click on the “Login” button.
Expected Result: User is redirected to the dashboard successfully.
How to Write Effective Test Cases
| How to Write Effective Test Cases |
|---|
| 1. Understand the software requirements clearly. |
| 2. Write concise and clear test steps. |
| 3. Include both positive and negative scenarios. |
| 4. Use real or realistic test data. |
| 5. Make test cases reusable and easy to maintain. |
You Might Also Like
Test Case Lifecycle
| Test Case Lifecycle |
|---|
| 1. Design – Prepare the test case based on requirements. |
| 2. Review – Validate test case accuracy and completeness. |
| 3. Execution – Perform the test manually or via automation. |
| 4. Result Recording – Mark pass/fail with actual results. |
| 5. Maintenance – Update cases when requirements change. |
Best Practices for Creating Test Cases
- Write one test case for one specific scenario.
- Avoid overly complex steps in a single case.
- Use consistent naming conventions for tracking.
- Automate repetitive test cases where possible.
- Review test cases with peers for accuracy.
Manual vs Automated Test Cases
| Aspect | Manual Test Cases | Automated Test Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Speed | Slower, requires human effort | Fast and repeatable |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost, cheaper long-term |
| Flexibility | Handles exploratory testing easily | Good for repetitive and regression testing |
| Accuracy | Prone to human error | Highly accurate and consistent |
| Maintenance | Easier for small projects | Better for large-scale applications |
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Writing vague or unclear steps.
- Ignoring edge cases or error scenarios.
- Creating duplicate or redundant test cases.
- Failing to update test cases after requirement changes.

Want flawless web performance through automated testing?
Importance of Test Cases in QA
| Importance of Test Cases in QA |
|---|
| Ensures thorough testing and reliable software quality. |
| Serves as documentation for the testing process. |
| Helps stakeholders understand testing scope and coverage. |
| Reduces risks of production failures and customer complaints. |
FAQs
Q1: What is a test case in simple terms?
A: A test case is a written set of steps and expected results used to verify that a software feature works correctly.
Q2: How many test cases should be written?
A: Enough to cover all functional requirements, edge cases, and critical scenarios.
Q3: Can test cases be automated?
A: Yes, repetitive and regression test cases are often automated for speed and accuracy.
Q4: Who writes test cases?
A: QA testers, developers, or business analysts involved in software quality assurance.
Q5: What tools are used to manage test cases?
A: Tools like JIRA, TestRail, Zephyr, and Azure DevOps are commonly used.





