IoT vs M2M: Key Differences Explained
Updated on : 12 May 2025
Image Source: google.com
Table Of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. What Is the Meaning of IoT
- 3. In What Ways Does IoT Operate
- 4. What Is M2M and What Does It Represent
- 5. How Is M2M Technology Implemented
- 6. Key Differences Between M2M and IoT
- 7. How M2M and IoT Communication Systems Compare
- 8. Using IoT to Improve Your Business with Sumato
- 9. Choosing Between M2M and IoT for Your Organization
- 10. How Devices Communicate in IoT vs M2M
- 11. Business Benefits of Integrating IoT Solutions
- 12. M2M vs IoT: Which Solution Suits Your Needs Best
- 13. FAQs
Table Of Contents
Introduction
IoT vs M2M: Key Differences Explained: Imagine a world where devices talk to each other—IoT connects them globally for smart, data-driven decisions. M2M? It's like a secret conversation between devices in a private network.
What Is the Meaning of IoT
Image Source: google
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of physical objects (“things”) embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies to connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet.
Key Subpoints:
- 📱 Smart Connectivity
- Devices like smartphones, sensors, or appliances connect via the internet.
- (IoT vs M2M: Key Differences Explained – IoT uses internet-based communication, while M2M often relies on direct links.)
- 📡 Data Exchange
- IoT devices collect and share real-time data to improve efficiency.
- 🧠 Automation & Intelligence
- Enables smart systems that can automate tasks (e.g., smart homes, traffic control).
- 🏭 Diverse Applications
- Used in healthcare, agriculture, manufacturing, smart cities, etc.
- 🔐 Security & Privacy Challenges
- Since devices are interconnected, securing data is a major concern.
- (IoT vs M2M: Key Differences Explained – M2M is often more isolated and secure, while IoT is more open and versatile.)
In What Ways Does IoT Operate
| 🔍 Aspect | 📌 Description |
|---|---|
| Sensing | IoT devices use sensors to collect real-world data like temperature, motion, or humidity. |
| Connectivity | Devices connect to the internet or other networks to share the collected data. |
| Data Processing | Collected data is processed locally or on the cloud to extract useful insights. |
| Action | Based on analysis, IoT systems can trigger actions like alerts, automation, or adjustments. |
| Remote Access | Users can monitor and control IoT devices from anywhere via smartphones or computers. |
| Integration | IoT integrates with other systems like cloud platforms or AI tools for smarter operations. |
| Automation | IoT enables automatic responses to certain conditions without human intervention. |
| Monitoring | Continuous tracking of environments, systems, or assets in real time. |
| Security | IoT systems include protocols to protect data and device access from threats. |
| Scalability | IoT setups can grow by adding more devices without major system redesigns. |
What Is M2M and What Does It Represent
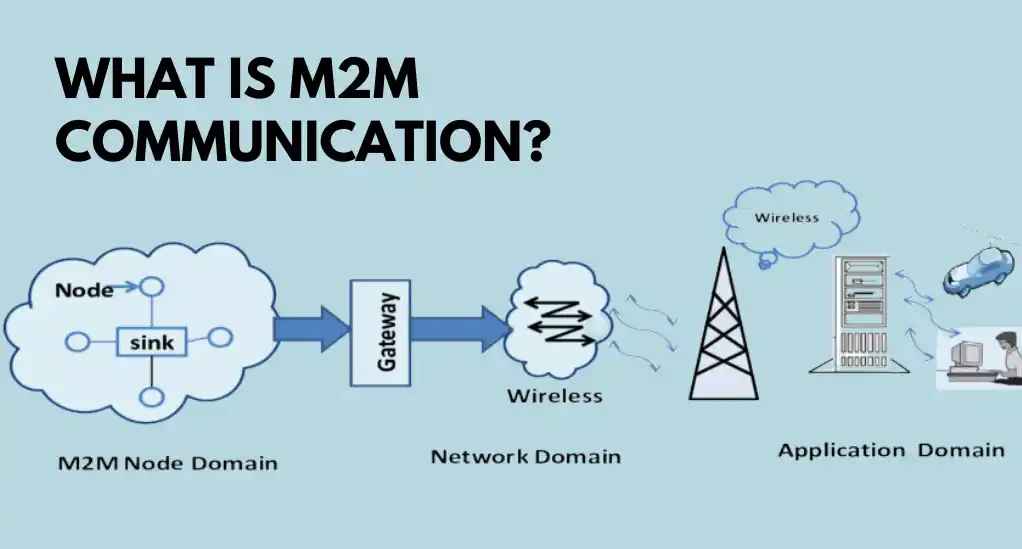
Image Source: google
| 🔹 Term | 📌 Meaning |
|---|---|
| M2M | Machine-to-Machine communication without human help. |
| Connection | Devices talk via cables, Wi-Fi, or cellular. |
| Use | Mainly in industries for automation and control. |
| Internet | Often works without internet. |
| Goal | Fast data sharing and task execution. |

Build intelligent, connected systems with our expert IoT solutions!
How Is M2M Technology Implemented
M2M technology is implemented using the following key components and steps:
- Sensors and Devices
- Devices collect data such as temperature, motion, or location.
- Communication Networks
- Data is sent through wired or wireless networks (like cellular or Wi-Fi).
- Data Transmission Modules
- M2M modules like modems or SIM cards handle data sending and receiving.
- Backend Systems
- Data is processed in control systems e.g., SCADA or cloud-based apps.
- Automation and Response
- The system reacts automatically, like sending alerts or adjusting machines.
In IoT vs M2M: Key Differences Explained, M2M is more focused on point-to-point automation without the need for internet or advanced analytics.
Unlike IoT, which enables smart decision-making across global networks, IoT vs M2M: Key Differences Explained shows that M2M is best for direct and local communication between machines.
Expert IoT App Development Services for Seamless Device Integration
Key Differences Between M2M and IoT
Image Source: google
| 🔹 Feature | 📡 M2M | 🌐 IoT |
|---|---|---|
| Connectivity | Point-to-point (wired/wireless) | Internet-based (IP networks) |
| Communication | Device to device | Device to cloud and beyond |
| Internet Dependency | Not required | Required |
| Data Handling | Limited, local | Advanced, cloud-based |
| Scalability | Low | High |
| Analytics | Minimal or none | Real-time, advanced analytics |
| Scope | Specific tasks, industrial use | Wider range – smart homes, cities, etc. |
| Human Interaction | Minimal | Supports user interfaces & apps |
| Integration | Standalone systems | Easily integrates with other platforms |
| Example | Remote meter reading | Smart thermostat with app control |
You Might Also Like
How M2M and IoT Communication Systems Compare
| 🔸 Aspect | 📡 M2M | 🌐 IoT |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Type | Device-to-device | Device-to-cloud and multi-device |
| Network Type | Private or closed networks | Internet-based networks |
| Data Flow | One-way or two-way | Two-way with cloud sync |
| Scalability | Limited | Highly scalable |
| Flexibility | Low | High with remote access |
| Data Processing | Local or centralized | Cloud-based, often real-time |
| Interoperability | Low (proprietary systems) | High (standard protocols) |
| User Interaction | Rare or none | User interfaces, mobile apps |
| Application Area | Industrial control, telemetry | Smart homes, health, cities |
| Technology Stack | Basic hardware + protocols | Sensors, cloud, AI, analytics |
Leading AI & ML Development Services to Elevate Your Business
Using IoT to Improve Your Business with Sumato
Sumato helps businesses grow smarter using IoT in the following ways:
- 1. Real-Time Monitoring
- Track assets, machines, or environments in real time to improve efficiency.
- 2. Predictive Maintenance
- IoT sensors detect issues early, reducing downtime and repair costs.
3. Smart Automation
- Automate repetitive tasks like lighting, security, or inventory checks.
4. Data-Driven Decisions
- Analyze IoT data to make better business choices and improve performance.
5. Remote Access and Control
- Manage systems and devices from anywhere using cloud-based IoT platforms.
In IoT vs M2M: Key Differences Explained, IoT allows broader smart business solutions, while M2M is limited to simple device-to-device tasks.
That’s why IoT vs M2M: Key Differences Explained highlights how IoT, especially through platforms like Sumato, gives businesses a competitive edge.
Choosing Between M2M and IoT for Your Organization

Image Source: google
| 🏢 Factor | 📡 M2M | 🌐 IoT |
|---|---|---|
| Use Case | Basic automation, monitoring | Smart operations, analytics |
| Internet Need | Not required | Required |
| Data Handling | Local or limited | Cloud-based, large-scale |
| Scalability | Less scalable | Highly scalable |
| Setup Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher but long-term value |
| Flexibility | Fixed functions | Adaptable and customizable |
| Integration | Standalone systems | Easily connects with other tech |
| Control | Limited remote control | Full remote access and control |
| Best For | Industrial tasks, telemetry | Smart business, IoT apps |
| Future Growth | Less adaptable | Future-ready and evolving |
Google Cloud Service: Secure and Scalable Solutions for Your Business
How Devices Communicate in IoT vs M2M
| 🔹 Aspect | 🌐 IoT | 📡 M2M |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Type | Device-to-cloud and multi-device | Device-to-device, point-to-point |
| Network | Internet-based, IP networks | Private networks, cellular, Wi-Fi |
| Data Flow | Two-way with cloud sync | One-way or two-way between devices |
| Data Processing | Cloud or edge processing | Local or centralized processing |
| Connectivity | Relies on global networks | Uses direct communication links |
| Internet Requirement | Requires internet connection | May not require internet |
| Protocols | HTTP, MQTT, CoAP, etc. | Proprietary or standard protocols like SMS, TCP/IP |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Limited scalability |
| Application | Smart homes, cities, businesses | Industrial automation, telemetry |
| Latency | Low latency with cloud processing | Low latency, direct communication |

Looking to transform your business with cutting-edge IoT solutions?
Business Benefits of Integrating IoT Solutions

Image Source: google
IoT helps businesses grow smarter and more efficient in many ways:
1. Real-Time Insights
- Monitor operations and assets live, enabling quicker decisions.
2. Cost Reduction
- Lower energy use, prevent equipment failures, and reduce downtime.
3. Improved Efficiency
- Automate tasks and streamline workflows to boost productivity.
4. Better Customer Experience
- Offer personalized services and faster response times using smart data.
5. Remote Monitoring & Control
- Manage devices and systems from anywhere, anytime.
6. Enhanced Security
- Use smart sensors to detect risks and improve safety.
As highlighted in IoT vs M2M: Key Differences Explained, IoT offers broader capabilities than M2M, especially in analytics and user interaction.
That’s why businesses looking to innovate prefer IoT – and IoT vs M2M: Key Differences Explained shows exactly how it adds long-term value.
M2M vs IoT: Which Solution Suits Your Needs Best
| 🔸 Criteria | 📡 M2M | 🌐 IoT |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Simple, direct device communication | Smart, connected ecosystems |
| Internet Required | No | Yes |
| Communication | Point-to-point | Device-to-cloud and multi-device |
| Scalability | Low | High |
| Data Processing | Local or centralized | Cloud or edge-based |
| User Interface | None or minimal | Supports apps and dashboards |
| Flexibility | Limited | Highly adaptable |
| Integration | Standalone systems | Integrates with other platforms |
| Use Cases | Industrial monitoring, telemetry | Smart homes, healthcare, business automation |
| Long-Term Value | Limited to current setup | Future-ready with expansion options |
FAQs
Q.1. What is the main difference between IoT and M2M?
A : M2M connects devices directly; IoT connects devices to the internet and cloud.
Q.2. Does M2M need the internet?
A : No, M2M often works without internet access.
Q.3. Is IoT more scalable than M2M?
A : Yes, IoT supports large networks and global access.
Q.4. Which one is better for smart homes?
A : IoT is better as it allows remote control and automation.
Q.5. Can M2M process data in the cloud?
A : Not usually — it processes data locally or on-site.
Q.6. Which is easier to set up?
A : M2M is easier and cheaper for small, simple tasks.
Q.7. Does IoT support apps and user interfaces?
A : Yes, IoT often includes dashboards and mobile apps.
Q.8. Are IoT and M2M used together?
A : Yes, IoT can include M2M components as part of its system.






