Difference Between TCP/IP Protocol and OSI Model
Updated on : 1 May 2025

Image Source: google.com
Table Of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. What is the TCP/IP Protocol?
- 3. What is the OSI Model?
- 4. Core Differences Between TCP/IP and OSI
- 5. Layers of the TCP/IP Model
- 6. Layers of the OSI Model
- 7. TCP/IP Protocol Suite Components
- 8. OSI Model Layer Functions
- 9. Real-World Usage of TCP/IP
- 10. Educational Use of the OSI Model
- 11. Skills Needed to Understand Each Model
- 12. Practical Examples and Comparisons
- 13. Difference Between TCP/IP Protocol and OSI Model Summary of Key Points
- 14. FAQs
Table Of Contents
Introduction
Ever wondered how your data travels online? 🌐 Let’s explore the Difference Between TCP/IP Protocol and OSI Model—TCP/IP powers real networks, while OSI is a learning tool. 🧠💻 Discover how they connect our digital world, layer by layer, in this networking journey!
What is the TCP/IP Protocol?
Image Source: google
TCP/IP is a set of rules for data exchange over networks. The Difference Between TCP/IP Protocol and OSI Model is that TCP/IP is practical, while OSI is theoretical and used for learning network layers.
🔹 Key Points:
-
📦 Protocol Suite: Not a single protocol, but a group working together for data transmission.
-
🛠️ Developed for the Internet: Created in the 1970s by the U.S. Department of Defense for secure, reliable networking.
-
🧱 4 Layers of TCP/IP:
- 🌐 Application Layer – User-facing services (e.g., HTTP, FTP).
- 📨 Transport Layer – Ensures reliable data transfer (TCP, UDP).
- 🛰️ Internet Layer – Routes data packets (IP).
- 🔌 Network Access Layer – Handles physical data transmission.
-
🔄 Standard for Networking: Forms the backbone of the modern internet and LANs.
-
✅ Reliable Communication: TCP ensures data is delivered accurately and in order.
What is the OSI Model?
Image Source: google
The OSI Model is a conceptual framework that explains how data moves in a network. It plays a key role in understanding the Difference Between TCP/IP Protocol and OSI Model by breaking communication into 7 clear layers.
🔹 Key Points:
-
📚 Theoretical Model: Unlike TCP/IP, OSI is not a protocol suite but a reference model used to understand and design network systems.
-
🧱 7 Layers of OSI (each layer performs a specific role):
- 🖥️ Application Layer – Interfaces with user applications (e.g., browsers).
- 📄 Presentation Layer – Translates data (encryption, encoding).
- 🗣️ Session Layer – Manages sessions between devices.
- 📤 Transport Layer – Ensures complete data delivery.
- 📬 Network Layer – Handles routing and addressing (like IP).
- 📦 Data Link Layer – Manages node-to-node data transfer.
- 🔌 Physical Layer – Transmits raw bits over hardware (cables, signals).
-
🎯 Purpose: Helps standardize network functions so devices and protocols can work together.
-
🛠️ Used for Learning & Design: A vital tool for network engineers, students, and developers to understand communication flow.
Core Differences Between TCP/IP and OSI
| 🌍 Aspect | 📝 TCP/IP Model | 💡 OSI Model |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Practical, used for real-world network communication | Theoretical, used as a reference model |
| Layers | 4 layers | 7 layers |
| Developed By | U.S. Department of Defense | ISO (International Organization for Standardization) |
| Protocol Dependency | Protocol-oriented | Model-oriented (no protocols defined) |
| Transport Layer | Uses TCP and UDP | Uses TCP-like and UDP-like functionalities |
| Network Layer | Supports only connectionless communication (IP) | Supports both connectionless and connection-oriented communication |
| Model Type | Implementation model | Conceptual/Reference model |
| Flexibility | More flexible and widely adopted | More rigid and mostly educational |
| Usage | Widely used in Internet and networks | Mainly used for teaching and protocol design |
Layers of the TCP/IP Model
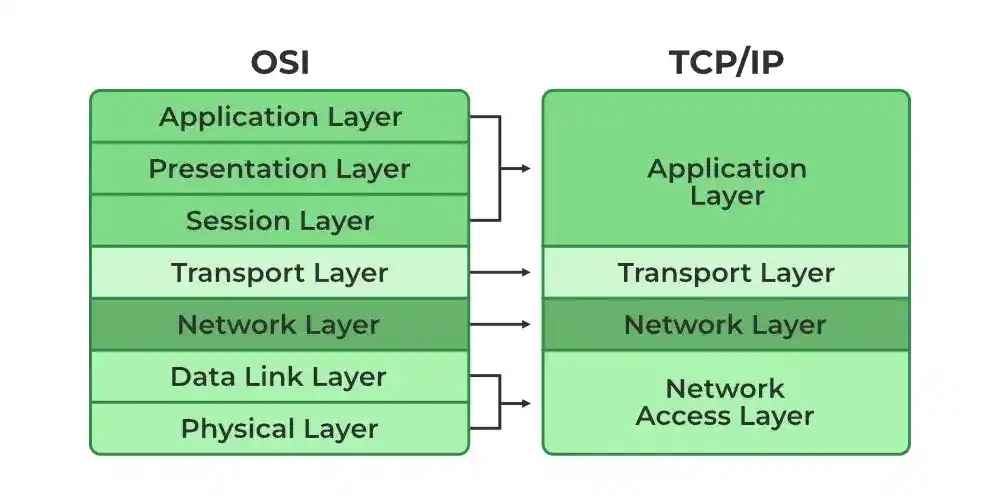
Image Source: google
| 🌍 Layer | 📝 Description | 💡 Example |
|---|---|---|
| Application Layer | Handles user-facing services and protocols like HTTP, FTP, DNS | Web browsers, Email clients, File transfer |
| Transport Layer | Ensures reliable data transmission with protocols like TCP and UDP | Web browsing (TCP), Streaming (UDP) |
| Internet Layer | Responsible for routing and addressing using IP | IP, Routing, Packet forwarding |
| Network Access Layer | Deals with hardware and physical transmission of data | Ethernet, Wi-Fi, Cellular networks |

AWS is Revolutionizing Mobile App Development with Scalable & Secure Solutions!
Layers of the OSI Model
| 🌍 Layer | 📝 Description | 💡 Example |
|---|---|---|
| Application Layer | Interfaces with user applications and provides network services | HTTP, FTP, DNS, Email protocols |
| Presentation Layer | Translates, encrypts, and compresses data for the application layer | Encryption (SSL/TLS), Data compression |
| Session Layer | Establishes, manages, and terminates communication sessions | NetBIOS, RPC, SMB |
| Transport Layer | Ensures reliable data transfer with error correction and flow control | TCP, UDP |
| Network Layer | Routes data packets across networks and handles addressing (IP) | IP, Routing protocols (e.g., RIP, OSPF) |
| Data Link Layer | Ensures error-free data transfer between two directly connected nodes | Ethernet, MAC addresses, Switches |
| Physical Layer | Transmits raw bitstreams over physical media (cables, radio waves) | Cables (Ethernet, Fiber), Wireless signals |
You Might Also Like
TCP/IP Protocol Suite Components
The TCP/IP Protocol Suite is a set of communication protocols based on a four-layer model used for data transmission across networks like the Internet. The key Difference Between TCP/IP Protocol and OSI Model is that TCP/IP is practical, while OSI is conceptual and educational.
1. Application Layer 🖥️
- Purpose: Directly interacts with user applications to facilitate communication.
- Key Protocols:
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) – for web browsing.
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol) – for transferring files.
- DNS (Domain Name System) – for resolving domain names to IP addresses.
2. Transport Layer 📦
- Purpose: Ensures data is transferred reliably between devices.
- Key Protocols:
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) – ensures reliable, error-free data transfer.
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol) – used for faster, connectionless communication (e.g., video streaming, gaming).
3. Internet Layer 🌍
- Purpose: Responsible for addressing, routing, and delivering packets across networks.
- Key Protocols:
- IP (Internet Protocol) – handles packet addressing and routing.
- ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) – used for error reporting and network diagnostics (e.g., ping).
4. Network Access Layer 🔌
- Purpose: Handles the physical connection between devices and the network.
- Key Protocols:
- Ethernet – commonly used in local area networks (LAN).
- Wi-Fi – for wireless connections.
OSI Model Layer Functions
The OSI Model (Open Systems Interconnection) is a 7-layer framework that explains how data moves through a network. It helps in understanding the Difference Between TCP/IP Protocol and OSI Model by detailing each layer's role in communication.
1. Application Layer 🖥️
- Purpose: Provides the interface between the user and the network.
- Function: Handles user interactions, application services, and network protocols.
- Examples: HTTP, FTP, DNS.
2. Presentation Layer 🎨
- Purpose: Ensures data is in a usable format for the Application Layer.
- Function: Translates, encrypts, and compresses data. It makes sure the data is readable and secure.
- Examples: Encryption (SSL/TLS), Data compression.
3. Session Layer 🗣️
- Purpose: Manages sessions between communicating devices.
- Function: Establishes, maintains, and ends communication sessions.
- Examples: NetBIOS, RPC (Remote Procedure Call).
4. Transport Layer 📦
- Purpose: Provides reliable data transfer between devices.
- Function: Ensures error-free transmission, flow control, and data sequencing.
- Examples: TCP, UDP.
5. Network Layer 🌍
- Purpose: Handles the routing of data across multiple networks.
- Function: Addresses and routes data packets to their correct destinations.
- Examples: IP (Internet Protocol), Routing protocols (e.g., RIP, OSPF).
6. Data Link Layer 🔗
- Purpose: Provides reliable transfer of data between two directly connected devices.
- Function: Handles error correction and data frame synchronization.
- Examples: Ethernet, MAC addresses, Switches.
7. Physical Layer 🔌
- Purpose: Transmits raw binary data over physical media.
- Function: Converts data into electrical or optical signals for transmission across cables or wireless channels.
- Examples: Cables (Ethernet, Fiber), Wi-Fi signals, Radio waves.
Real-World Usage of TCP/IP
| 🌍 Application | 📝 Description | 💡 Real-World Example |
|---|---|---|
| Web Browsing | Used for accessing websites and transferring web data | HTTP and HTTPS for browsing (Google, Facebook) |
| Email Communication | Enables the sending and receiving of emails | SMTP for sending, IMAP/POP3 for receiving |
| File Sharing | Allows sharing of files over networks | FTP for file transfers between systems |
| Streaming Media | Used for video and audio streaming over the internet | RTSP or HTTP used by Netflix, YouTube |
| Voice over IP (VoIP) | Enables voice communication over the internet | Skype, Zoom, WhatsApp calls |
| Remote Access | Used for remote control of devices and servers | SSH for server access, VPNs for secure remote access |
| Online Gaming | Enables multiplayer gaming over the internet | UDP used for games like Fortnite, Call of Duty |
| Cloud Computing | Facilitates access to online services and storage | AWS, Google Cloud using TCP/IP stack |
| IoT (Internet of Things) | Connects smart devices and sensors to the internet | Smart thermostats, lights using TCP/IP |
| Data Backup | Ensures data is securely backed up over a network | Cloud backups via Google Drive, Dropbox |
Professional IoT Application Development for Smooth and Smart Device Connectivity
Educational Use of the OSI Model
| 🎓 Purpose | 📝 Description | 💡 Example/Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Teaching Networking Concepts | Helps students understand how data flows in a network | Visualizing step-by-step data movement across 7 layers |
| Protocol Layering | Clarifies the function of each layer and their interactions | Understanding how TCP works at Transport Layer and IP at Network Layer |
| Troubleshooting Networks | Assists in identifying issues by checking layer-wise functionality | Diagnosing connectivity vs configuration issues |
| Standardized Communication | Provides a universal reference for network discussions | Ensures consistent terminology among students and instructors |
| Exam Preparation | Commonly used in academic assessments and certifications | Questions like 'match the layer with its function' |
| Curriculum Structuring | Allows educators to break down complex topics by layer | Separate lessons on Transport Layer or Data Link Layer |
Skills Needed to Understand Each Model
| 🧠 Skill Area | 🌐 TCP/IP Model | 📶 OSI Model |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Networking Concepts | Required to grasp how internet communication works | Essential for understanding network flow layer-by-layer |
| Layered Architecture | Understanding 4-layer structure | Understanding 7-layer detailed structure |
| Protocol Knowledge | Familiarity with TCP, IP, UDP, HTTP | Knowledge of protocols like FTP, SMTP, and more per layer |
| Troubleshooting Skills | Helpful for diagnosing connectivity issues | Useful for pinpointing specific layer failures |
| Practical Application | Focus on real-world networking and internet protocols | Ideal for theoretical understanding and education |
| System Administration | Useful for configuring network devices and firewalls | Helpful for identifying communication issues layer-wise |
| Packet Analysis | Basic understanding of packet headers and data flow | Deeper analysis by isolating issues at specific OSI layers |
| Certifications (e.g., CCNA) | Required for understanding protocol suite | Often based heavily on OSI layer model |
| Security Understanding | Helps understand encryption at Transport & Application layers | In-depth understanding at Presentation & Session layers |

Want to Elevate Your Mobile App with Advanced Solutions?
Practical Examples and Comparisons
Understanding the Difference Between TCP/IP Protocol and OSI Model helps relate theory to real-world networking. TCP/IP is used in practical scenarios, while OSI provides a conceptual framework for learning, troubleshooting, and designing networks.
🔹 1. Protocol Usage
- TCP/IP Model: Used in real-world networking like the internet.
- Example: Sending an email (uses SMTP over TCP/IP).
- OSI Model: A conceptual guide used mostly for learning and troubleshooting.
- Example: Helps identify at which layer an error occurs (like IP conflict at Network Layer).
🔹 2. Real-World Application
- TCP/IP: Actual protocols implemented in devices (routers, switches, servers).
- Example: Web browsing with HTTP over TCP/IP.
- OSI: Ideal for understanding the "what" and "how" of communication.
- Example: Teaching how data travels from the Application to the Physical layer.
🔹 3. Troubleshooting Networks
- TCP/IP: Tools like
pingandtraceroutework based on this model. - OSI: Used to trace issues by layers—like DNS issues (Application Layer) vs. routing issues (Network Layer).
🔹 4. Layer Comparison
- OSI has 7 layers, more detailed (Presentation, Session).
- TCP/IP has 4 layers, more practical and condensed.
🔹 5. Use in Certifications
- OSI Model is heavily referenced in networking exams like CompTIA and CCNA.
- TCP/IP knowledge is essential for real-world networking jobs.
Strengthen Your iOS App with Hexadecimal Software Excellence
Difference Between TCP/IP Protocol and OSI Model Summary of Key Points
Image Source: google
- TCP/IP Model is a practical, 4-layer model used in real-world networks and the internet.
- OSI Model is a conceptual, 7-layer model used for understanding and teaching network communication.
- TCP/IP focuses on protocols and their implementation (e.g., TCP, IP, HTTP).
- OSI provides a detailed, structured approach with layers like Presentation and Session for better learning.
- TCP/IP is used in practice, while OSI is used more in theory and troubleshooting.
- Both models help in understanding how data is transmitted across networks.
- OSI is essential in certification training; TCP/IP is essential in real-world networking.
- Troubleshooting tools (like ping, traceroute) align more with TCP/IP, but issues are often diagnosed using OSI layers.
- OSI's layered clarity aids in isolating and solving network problems effectively.
- Both models complement each other, with OSI guiding structure and TCP/IP enabling communication.
FAQs
Q.1. What is the TCP/IP Model?
A : Its a 4-layer model used for real-world internet communication.
Q.2. What is the OSI Model?
A : Its a 7-layer theoretical model used to understand how networks work.
Q.3. Which model is used in real life?
A : TCP/IP is used in real-world networking.
Q.4. Which model is used for learning and exams?
A : OSI Model is commonly used for teaching and certifications.
Q.5. How many layers does TCP/IP have?
A : It has 4 layers: Application, Transport, Internet, and Network Access.
Q.6. How many layers does OSI have?
A : It has 7 layers: Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link, Physical.
Q.7. Is TCP/IP based on OSI?
A : No, it was developed independently, but both models are similar in structure.
Q.8. Can they work together?
A : Yes, OSI helps understand how TCP/IP works in practice.
Q.9. Which is easier to understand?
A : OSI is easier for beginners to learn networking layer by layer.
Q.10. Why are both important?
A : TCP/IP is used for actual communication, while OSI helps explain and troubleshoot it.






