Client Server System Architecture: A Complete Guide
Updated on : 4 AUGUST 2025
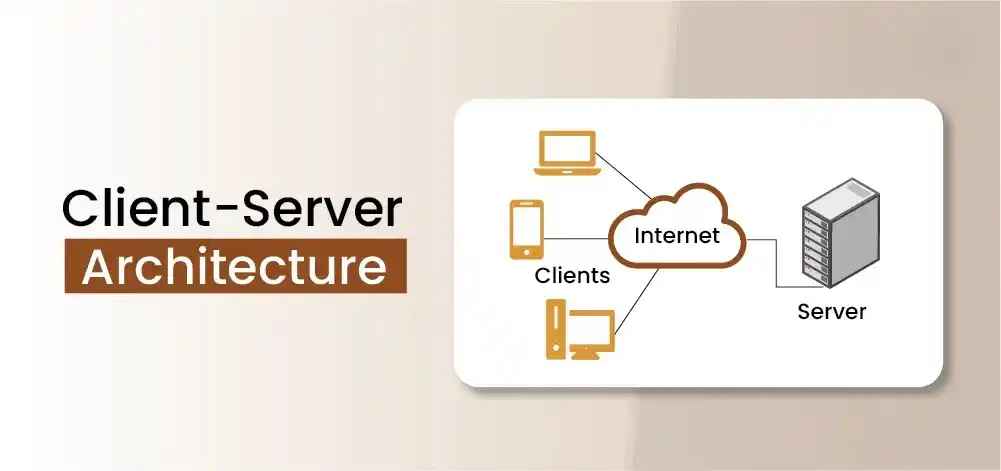
Image Source: google.com
Table Of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. What is Client-Server System Architecture
- 3. Components of Client-Server Architecture
- 4. Why Use Client-Server Architecture
- 5. Key Features of Client-Server Architecture
- 6. Types of Client-Server Architecture
- 7. How Client-Server Communication Works
- 8. Advantages of Client-Server Architecture
- 9. Limitations of Client-Server Architecture
- 10. Client-Server Architecture vs Peer-to-Peer
- 11. Real-World Examples of Client-Server Systems
- 12. FAQs
Table Of Contents
Introduction
Client-Server System Architecture is the backbone of modern networks. In this model, clients request services like data access, file sharing, or applications from a central server, which processes these requests and responds accordingly. This setup enhances efficiency, scalability, and security in computing systems.
What is Client-Server System Architecture
Image Source: google
| Client-Server Architecture |
|---|
| The client (user's device or application) sends requests for data or services. |
| The server (centralized computer) processes and returns the requested information. |
| 🌐 Centralized Control: Server stores and manages data centrally. |
| 🔗 Communication: Clients and servers interact over a network. |
| ⚙️ Service-Oriented: Server provides resources, processing power, and services. |
| 📡 Scalable: Supports multiple clients simultaneously. |
Components of Client-Server Architecture
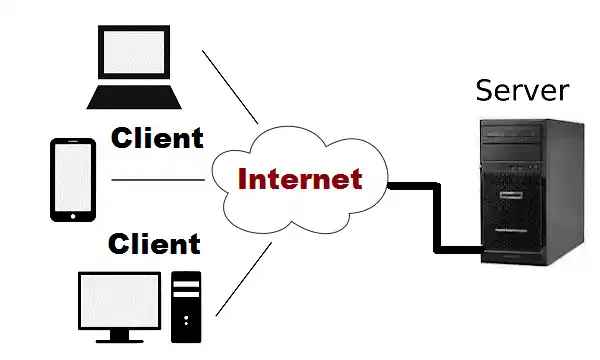
Image Source: google
The architecture is divided into two main components:
-
Client:
- User-facing application requesting data or services.
- Examples: Web browsers, mobile apps, desktop software.
-
Server:
- Central system storing data, handling requests, and providing services.
- Examples: Database servers, application servers, mail servers.
Why Use Client-Server Architecture
| Reason | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Centralized Management | Data and applications are controlled from a single server. |
| Scalability | Supports many clients without performance degradation. |
| Security | Central server provides controlled access and data protection. |
| Resource Sharing | Multiple clients can access shared files, databases, and applications. |

you want to hire SQL Developer?
Key Features of Client-Server Architecture
| Key Features of Client-Server Architecture |
|---|
| Two-Tier Communication: Clients and servers interact via requests and responses. |
| Data Security: Server manages authentication and permissions. |
| Reliability: Central server provides consistent data and services. |
| Multi-Client Support: Handles numerous client connections simultaneously. |
| Flexibility: Clients can be thin (lightweight) or thick (rich interface). |
Types of Client-Server Architecture
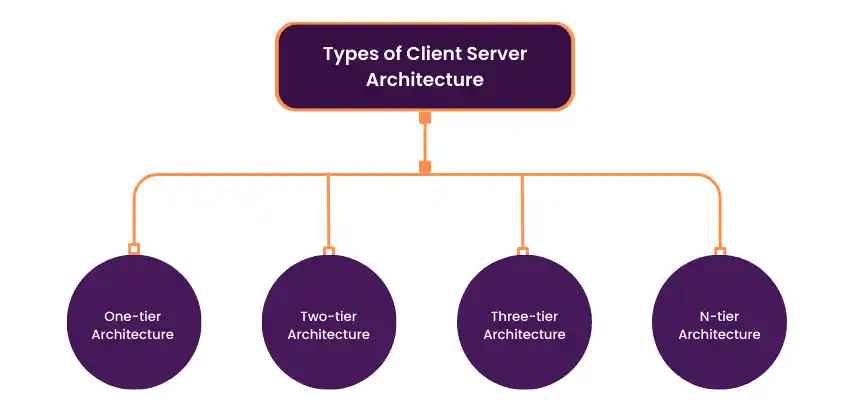
Image Source: google
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Two-Tier | Direct communication between client and server. | Web browser → Web server |
| Three-Tier | Includes a middle layer (application server) for processing. | Web browser → App server → Database server |
| N-Tier | Multiple layers for scalability and distributed services. | Enterprise applications with load balancers and servers |
How Client-Server Communication Works
- Client sends a request for data or a service.
- Server processes the request.
- Server sends a response back to the client.
- Communication often uses protocols like HTTP, FTP, or TCP/IP.
Advantages of Client-Server Architecture
| Advantages |
|---|
| Centralized data management ensures consistency. |
| Easy maintenance and backup of data. |
| Scalable to support many clients. |
| Enhanced security and controlled access. |
| Efficient sharing of resources and applications. |
You Might Also Like
Limitations of Client-Server Architecture
| Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
| Server Dependency | If the server fails, clients cannot access services. |
| Cost | Requires setup of dedicated server hardware and software. |
| Network Traffic | High client requests can overload the server. |
| Complex Management | Requires skilled administrators for configuration and maintenance. |

Looking mySQL Developer For your business?
Client-Server Architecture vs Peer-to-Peer
| Feature | Client-Server | Peer-to-Peer |
|---|---|---|
| Data Storage | Centralized server | Distributed across peers |
| Scalability | High, server supports many clients | Limited to small networks |
| Security | Centralized control, better protection | Less secure, depends on peers |
| Examples | Web applications, database systems | File sharing apps, torrents |
Real-World Examples of Client-Server Systems
- Web applications (Google, Amazon, Facebook)
- Email servers (Gmail, Outlook)
- Database servers (MySQL, Oracle)
- Online gaming platforms
FAQs
Q1. What is Client-Server Architecture?
A: A computing model where clients request services from a centralized server.
Q2. What are the main components of this architecture?
A: Client (requester) and Server (provider of resources).
Q3. What are 2-tier and 3-tier architectures?
A: 2-tier is direct client-server interaction, while 3-tier adds an application server in between.
Q4. What are its advantages?
A: Centralized control, scalability, data security, and resource sharing.
Q5. How does it differ from Peer-to-Peer?
A: In client-server, data is centralized; in P2P, data is shared directly among peers.





